Topological data model
Introduction
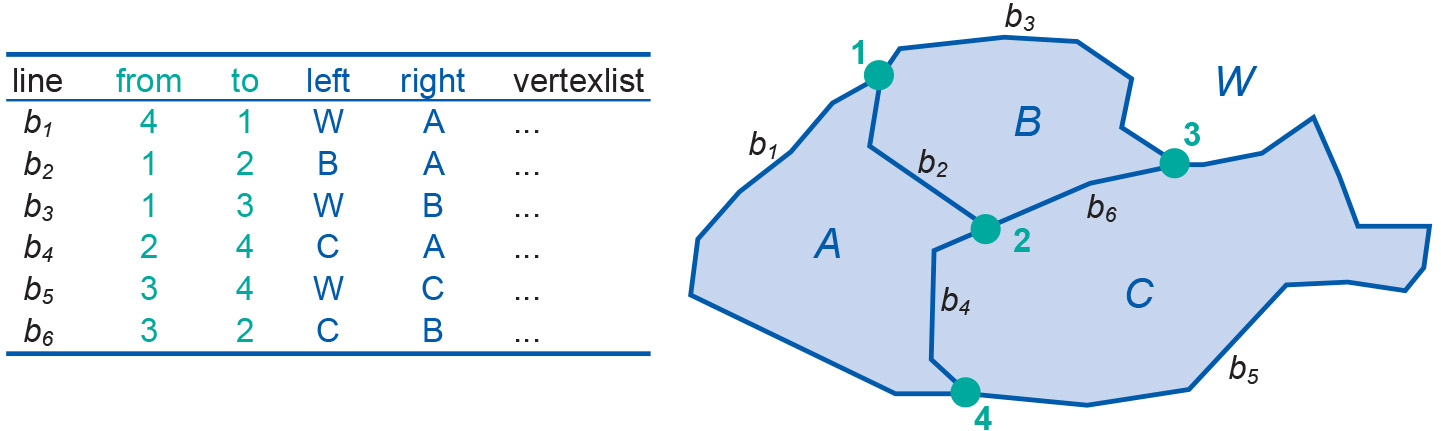
The boundary model is an improved representation that deals with the disadvantages of the naive polygon which is described in polygons. It stores parts of a polygon’s boundary as non-looping arcs and indicates which polygon is on the left and which is on the right of each arc. A simple example of the boundary model can be seen below. It illustrates which additional information is stored about spatial relationships between lines and polygons. Obviously, real coordinates for nodes (and vertices) will also be stored in another table. The boundary model is also called the topological data model as it captures some topological information, such as polygon neighbourhood, for example. You can read more about topological information in Topology. Observe that it is a matter of a simple query to find all the polygons that are the neighbour of a given polygon, unlike the case above.
Explanation
Synonyms
Boundary model
Learning outcomes
-
2 - Spatial data modelling: computer representations
Explain and be able to apply basic vector and raster spatial data structures including selecting a suitable data structure for geographic phenomena (level 1, 2 and 3).
-
3 - Spatial data modelling: topology
The student is able to describe and explain the concept of topology (level 1 and 2).
Prior knowledge
Outgoing relations
- Topological data model is used by Area representation
Incoming relations
- Topology is used by Topological data model