Ellipsoid
Introduction
The most convenient geometric reference surface for mapping purposes is the oblate ellipsoid (Figure 1). It provides a relatively simple figure of the Earth which fits the geoid to a first order approximation. An ellipsoid is formed when an ellipse is rotated about its minor axis. This ellipse which defines an ellipsoid or spheroid is called a meridian ellipse (notice that ellipsoid and spheroid are equivalent and interchangeable words).

Many different sorts of ellipsoids have been defined. Local ellipsoids have been established to fit the Geoid (mean sea level) well over an area of local interest, which in the past was never larger than a continent. This meant that the differences between the Geoid and the reference ellipsoid could effectively be ignored, allowing accurate maps to be drawn in the vicinity of the datum (Figure 2).
With increasing demands for global surveying, global reference ellipsoids are developed. In contrast to local ellipsoids, which apply only to a specific country or localized area of the Earth’s surface, global ellipsoids (GRS80, WGS84) approximate the Geoid as a mean Earth ellipsoid.
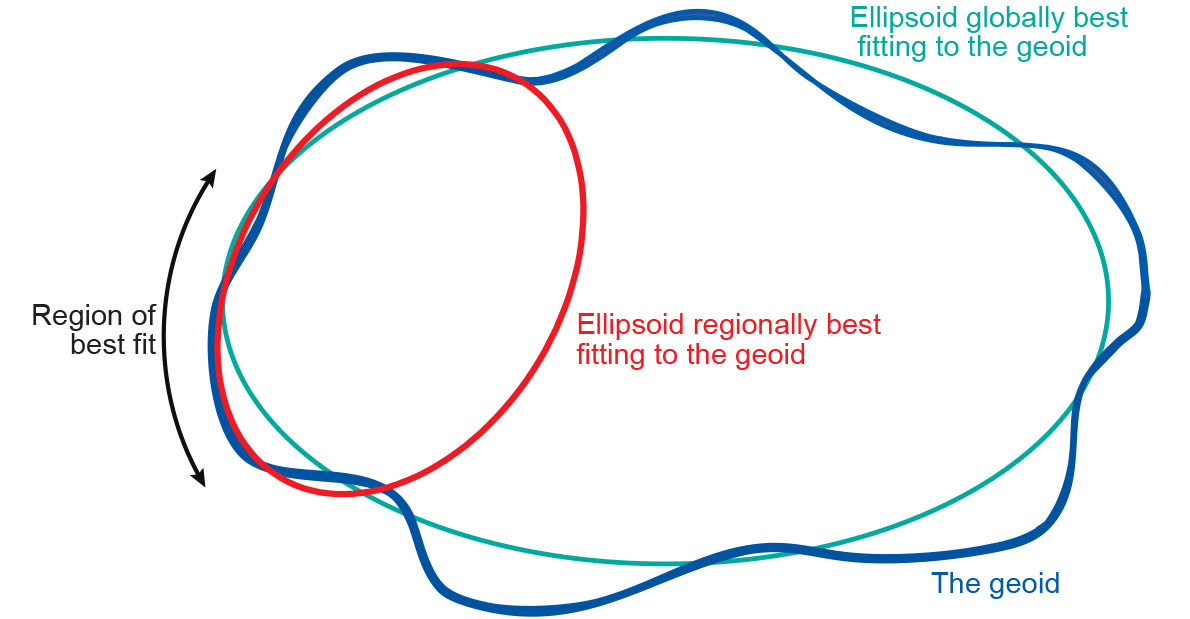
best-fit ellipsoid for a chosen region. Adapted from: Ordnance Survey of Great Britain. A Guide to Coordinate Systems in Great Britain.
Explanation
The shape of an ellipsoid may be defined in a number of ways, but in geodetic practice it is is usually defined by its semi-major axis and flattening (Figure 1). Flattening f is dependent on both the semi-major axis a and the semi-minor axis b:
The ellipsoid may also be defined by its semi-major axis a and its eccentricity e, which can be expressed as:
Given one axis and any one of the other three parameters, the other two can be derived. Typical values of the parameters for an ellipsoid are:
Learning outcomes
-
7 - Coordinate systems and map projections
Explain the relevance of reference surfaces, coordinate systems, and coordi-nate transformations in mapping (level 1 and 2).
Prior knowledge
Outgoing relations
- Ellipsoid is a kind of Reference surface
Incoming relations
- Global horizontal datum is modelled by Ellipsoid
- Global vertical datum is modelled by Ellipsoid
- Horizontal datum is modelled by Ellipsoid