Projections by secancy
Introduction
Another class of projections is obtained if the surfaces are chosen to be secant to (to intersect with) the horizontal reference surface. Then, the reference surface is intersected along one closed line (azimuthal) or two closed lines (cone and cylinder). Secant map surfaces are used to reduce or average out scale errors since the line(s) of intersection are not distorted on the map.
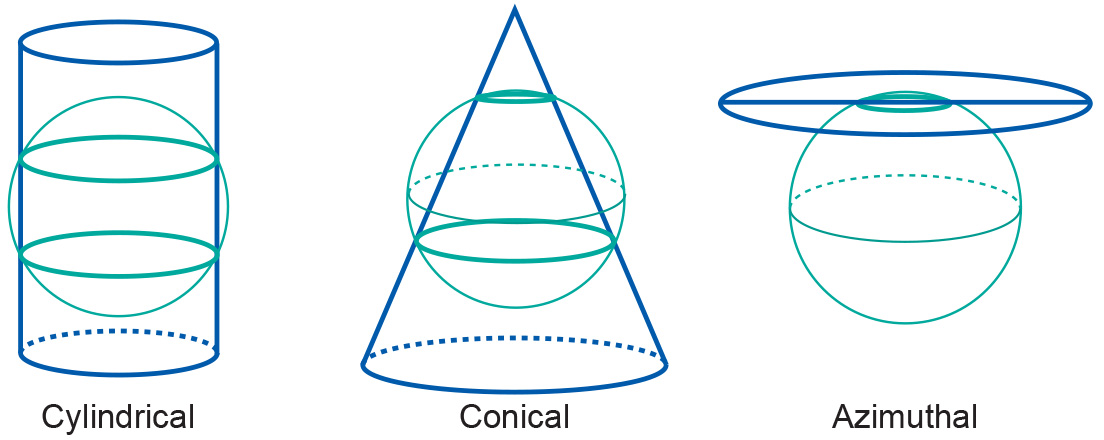
Examples
If an area is approximately circular, it is possible to create a map that minimizes distortion for that area on the basis of an azimuthal projection.
Learning outcomes
-
7 - Coordinate systems and map projections
Explain the relevance of reference surfaces, coordinate systems, and coordi-nate transformations in mapping (level 1 and 2).
Prior knowledge
Outgoing relations
- Projections by secancy is a kind of Projection classification