Changing map projection
Introduction
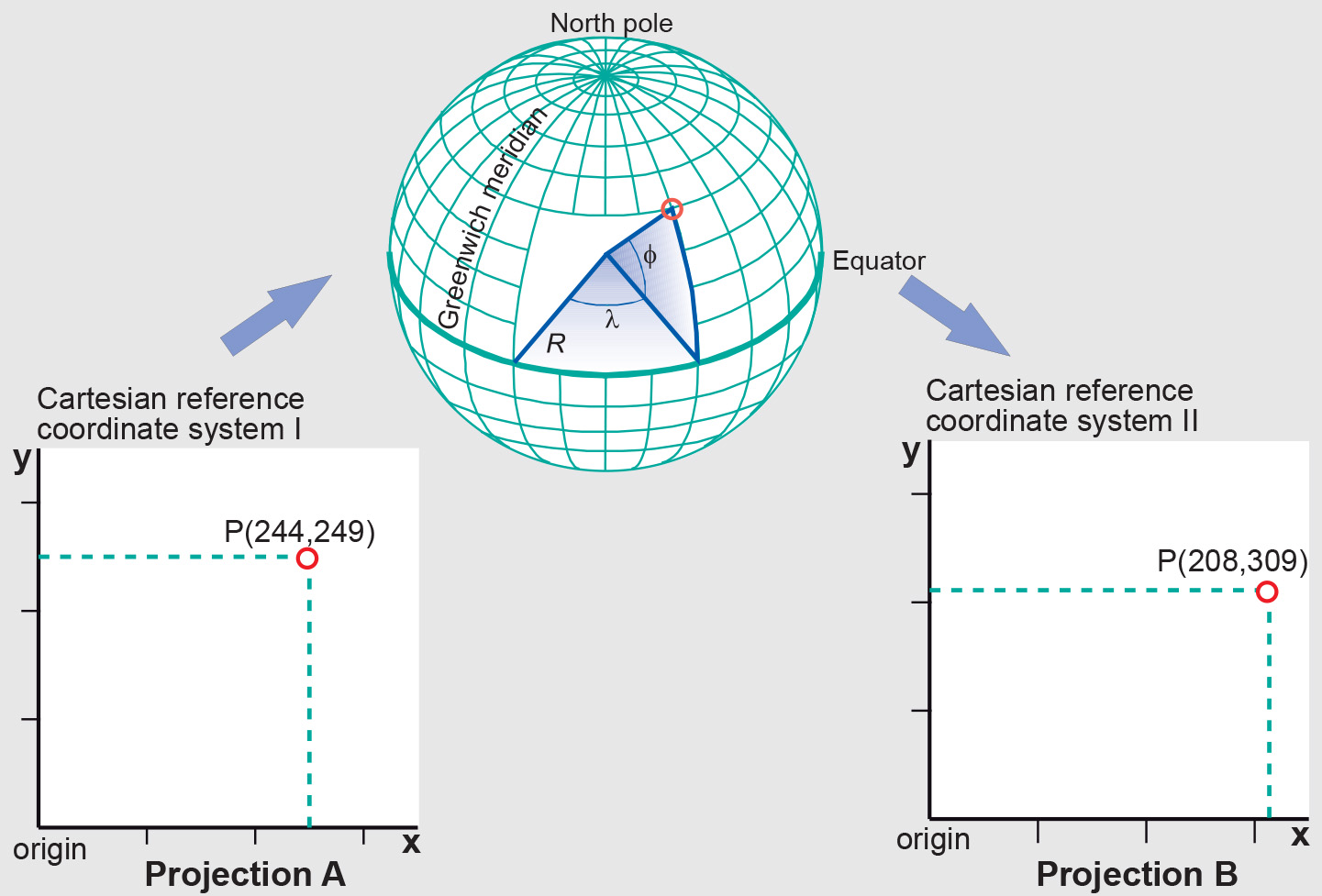
Forward and inverse mapping equations are normally used to transform data from one map projection into another. The inverse equation of the source projection is used first to transform source projection coordinates (x, y) to geographic coordinates (ϕ, λ). Next, the forward equation of the target projection is used to transform the geographic coordinates (ϕ, λ) into target projection coordinates (x′, y′). The first equation takes us from a projection A into geographic coordinates. The second takes us from geographic coordinates (ϕ, λ) to another map projection B.
Historically, GI Science has dealt with data referenced spatially with respect to the (x, y) coordinates of a specific map projection. For application domains requiring 3D spatial referencing, a height coordinate may be added to the (x, y) coordinates of the point. The additional height coordinate can be a height H above mean sea level, which is a height with a physical meaning. The (x, y, H) coordinates then represent the location of objects in a 3D space.
Prior knowledge
Outgoing relations
- Changing map projection is part of Coordinate transformation