Co-registration
Introduction
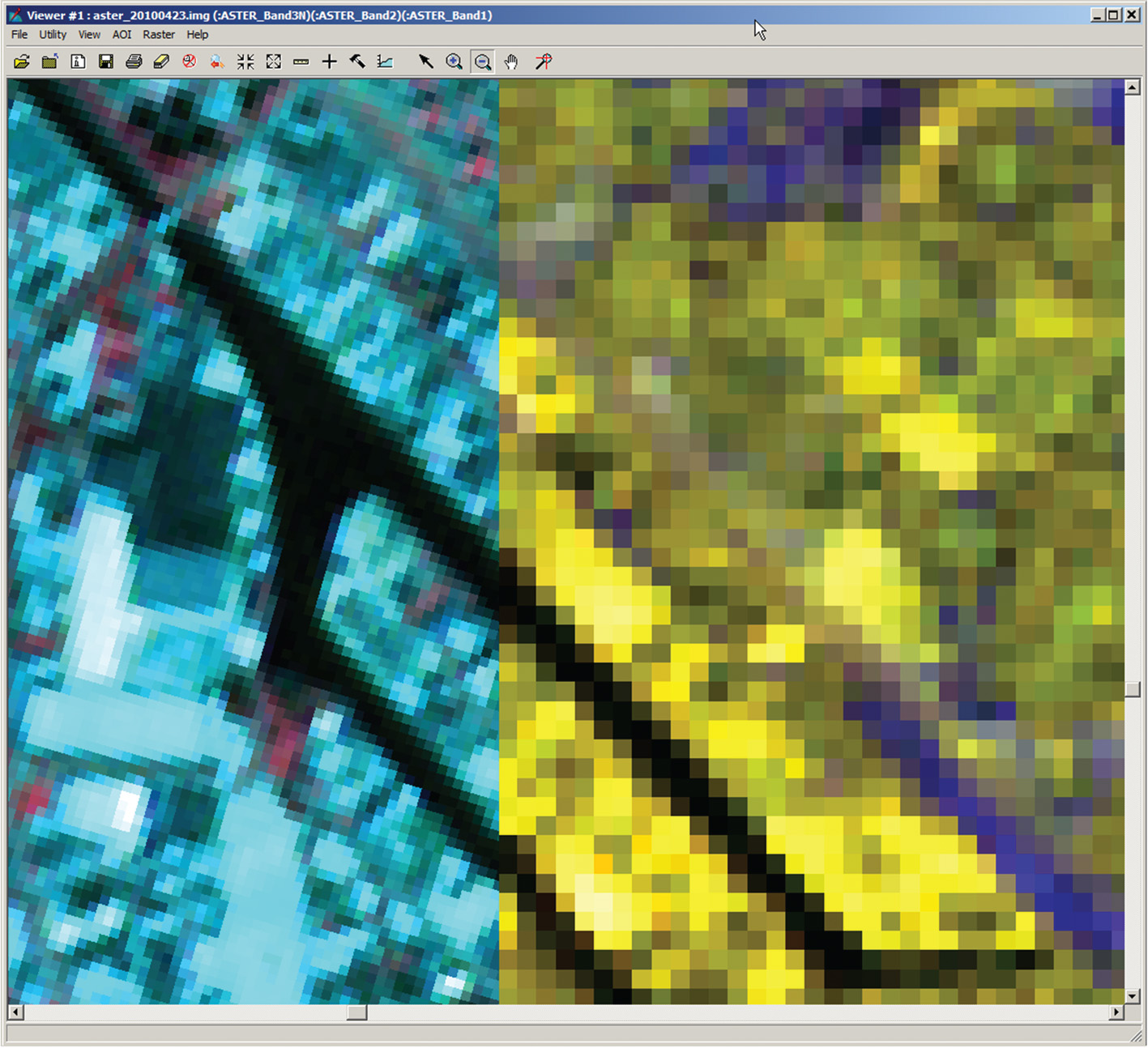
Analysing multiple layers of geospatial data in a meaningful and coherent way requires the co-registration of all these layers to a common spatial grid or reference. The common grid spacing chosen is application-dependent and several considerations may play a role in that choice. In some cases the preservation of high levels of spatial detail is most important, and in other cases high levels of radiometric precision may be more relevant. In the first instance, one would probably choose a common grid spacing that accommodates the data layer with the highest spatial resolution, while in the second instance one may choose a grid with a wider spacing. Figure 1. illustrates the display of two images with different grid spacing and orientation for a part of Enschede. The images are co-registered, yet the pixel size and orientation are different.
Outgoing relations
- Co-registration is part of Requirements of data integration
- Co-registration is used by Data integration