Merging datasets
Introduction
Merging data sets occurs when individual data sets have been prepared they sometimes have to be integrated into a single, “seamless” data set, whilst ensuring that the appearance of the integrated geometry is as homogeneous as possible. Edge matching is the process of joining two or more map sheets, for instance, after they have been separately digitized.
Merging adjacent data sets can be a major problem. Some GIS functions, such as line smoothing and data clean-up (removing duplicate lines) may have to be performed. The Figure below illustrates a typical situation. Some
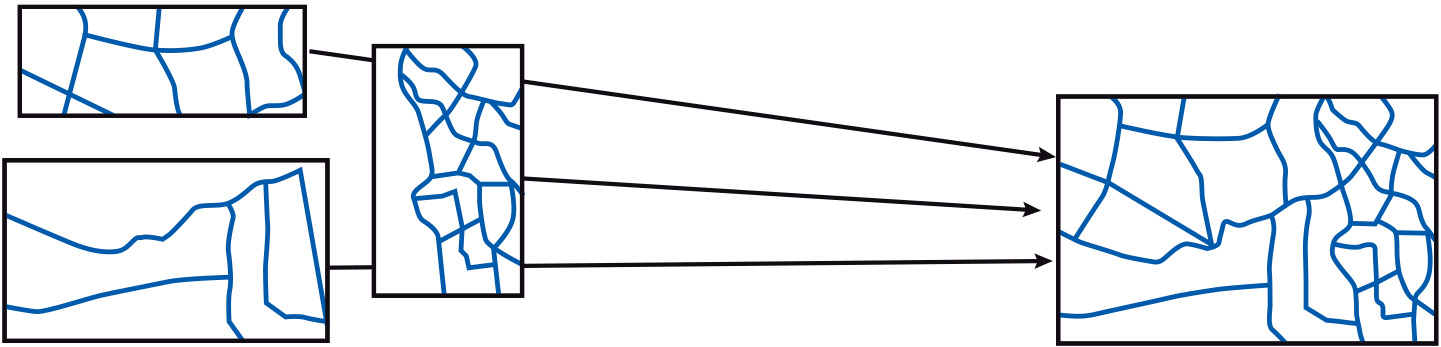
Coordinates of the objects along shared borders are adjusted to match those in the neighbouring data sets. Mismatches may still occur, so a visual check and interactive editing is likely to be required.
Prior knowledge
Outgoing relations
- Merging datasets is part of Combining data from multiple sources